INTRODUCTION
In the technical inspections we carry out of buildings, they have a very common deficiency: the lack of thermal insulation of the facades.
The lack of insulation causes condensation on the facades and an excess of energy consumption.
Saving energy today represents one of the most important objectives that arise both in the design of new buildings and in the rehabilitation of existing buildings. Energy (electricity, gas and other fuels) is becoming more expensive and building regulations are increasingly demanding.
The thermal insulation of a building is essential both to minimize energy consumption and to improve comfort and well-being for the home user. The pathologies associated with the absence of isolation are many. In this article we talk about mold .
There are 3 ways to perform the intervention in the classification of facade insulation systems:
- Insulate on the inside of the façade
- Insulate on the inside face of the façade
- Insulate on the outer face of the facade
Currently there are multiple thermal insulation solutions, however, not all have the same performance or the same advantages. Next, we will explain to you which are the main insulation systems on the market, for buildings already built. All buildings have characteristics that make them unique and it will always be necessary for the technicians to carry out a preliminary study to determine which system is the most appropriate in each case. That said, we provide some basic guidelines to decide which system is more to your liking.
In addition to spending less and recovering the investment in a few years, the reform with isolation can make you get public aid for the rehabilitation of buildings.
INSULATE INSIDE THE FACADE
INJECTION OF THERMAL INSULATION IN THE AIR CHAMBER
This system is ideal in cases where a rehabilitation of the exterior facade cannot be carried out, usually due to disagreements in the neighborhood community. It allows us to isolate our home without affecting the rest of the neighbors.
Step 1. Section of the facade without insulation:

Step 2. Section of the facade with the insulation:

The procedure requires an interior air chamber in the façade and consists of injecting thermal insulating material inside the chamber. This is achieved by injection guns and compressed air, which introduce the material through holes that will have been made with a drill every half meter approximately, filling the chamber with the insulating material in the form of foam or small balls of the material (EPS per example). Insertion of the material into the air chamber through the holes every 50cm.
This system is undoubtedly the most economical and does not require renovation either on the outside or on the inside.
However, this system has several drawbacks that must be taken into account. The insulation will not be homogeneous, leaving some areas with a higher insulation density, in addition, thermal bridges are not eliminated and in cases where efficient ventilation is not available, the appearance of condensation humidity is possible.
At the end of the energy improvement of our facade with this system, it will always be necessary to carry out a small repair and a painting on the wall in which the holes for the injection have been made.
Most commonly used insulation materials in façade air chamber fillings
Blown rock wool
Fine rock wool for blowing is a material derived from volcanic stone and coal in the form of rock wool nodules by weight, therefore, it can be blown between partitions and walls. In addition, it has class of reaction to fire A1 (Euro Class) therefore it is non-combustible.

Inflated EPS
It is the recommended insulating material in narrow chambers or very fine and irregular cavities. Resistant to water and incorporates a special graphite treatment that modifies thermal radiation by reflecting it. It is a reusable thermal insulator with good durability. It is suitable for extreme temperature environments in winter.

Insuffled cellulose
Cellulose is a thermal insulator made up of a ground recycling compound (usually newspaper) and salts that give it insecticidal, fire retardant and antifungal properties. It is a very good thermal and acoustic insulator; effective for winter due to its low thermal conductivity.
Effective for the summer as it has an enormous capacity to store heat, with an inertia close to 12 hours. So it has a great behavior in summer, giving up part of the heat accumulated throughout the day and night.
On the other hand, it regulates humidity, since it has the capacity to store it, it is an ecological material and therefore requires little energy for its manufacture.

Advantages and disadvantages of insulating inside the air chamber of the facade
Advantages:
– It does not require a rehabilitation on the outside or inside of the facade.
– Allows to isolate dwellings independently from the rest of the building.
– It is the system with a faster application.
– It is the most economical system.
Disadvantages:
– It does not eliminate thermal bridges, humidity can be generated by condensation.
– It does not ensure homogeneity in its application, some areas of the house will be rather isolated.
– An air chamber is required on the facade.
INSULATE INSIDE. ADDITION OF INSULATING LAYER ON INSIDE THE FACADE; REMOVED.
This system is ideal in cases where it is not possible to carry out a rehabilitation on the outside of the façade and there is no air chamber either. This method is usually the only viable option for those buildings with facades classified as historical heritage.
It consists of building a layer of thermal insulation, directly on the inside face of the façade. There are two interior cladding systems.
Step 1. Section of the facade without insulation:

Step 2. Section of the facade with the insulation:

1.Direct transfer
The insulation is applied directly to a support base (strong to ensure stability) by mechanical fasteners, and to it, bonded drywall. A paint finish is applied to these panels.

2. Self-supporting cladding
The thermal insulation plates are placed between the uprights of the self-supporting auxiliary structure (which can be made of galvanized steel or wood) of the laminated gypsum panels, mechanically fixed to the profiles. Finally, a paint is applied as the final finish of the panels. Being self-supporting, it does not use the enclosure as a support. In these cases it is advisable to place a vapor barrier (polyethylene for example) before the plasterboard; It depends on the climate where our building is located, this is essential.

Although this system achieves the objective of thermally insulating our home, the internal thermal insulation system by means of cladding has some drawbacks to take into account, such as that it does not solve the problems of thermal bridges and that it generates a small loss of Useful surface in the house. This loss of surface is due to the increase in the thickness of the walls, approximately between 5-10cm.
Most used insulation materials in cladding
1.Rock wool
The mineral wool insulation (glass wool or rock wool) in cladding is installed in the form of semi-rigid panels and is placed between the metal profiles of the self-supporting cladding system.

2. Expanded polystyrene (EPS)
Expanded polystyrene or EPS is a cellular and rigid plastic material, foamed (contains air) and is used in the building sector as a thermal and acoustic insulator.
It is generally installed by means of the direct cladding system, when the existing enclosure serves as a support.

3. Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
The XPS sheets are glued to the existing support by means of an adhesive (cement-glue), and optionally also with mechanical fixings. As a final coating, a black plaster trim is applied, and over it, white plaster.

4. Polyurethane
It is a material with high insulating capacity and durable over time (25 years). Generally it is applied by projecting the polyurethane, or with shaped plates (very common in sandwich panels) on which laminated plasterboards are installed. When the lining is direct, it can be executed with polyurethane sheet and plasterboard assemblies, or by executing a projection in situ.

Advantages and disadvantages of insulating from the inside
Advantages:
– Allows homogeneous isolation throughout the application area.
– Allows to isolate dwellings independently from the rest of the building.
– It is applicable to homes with historic protection facades.
Disadvantages:
– It does not eliminate thermal bridges, humidity can be generated by condensation.
– Annoyances are generated for the users of the building, when carrying out works inside the house.
– Slight loss of useful surface in the house, enlargement of the facade thickness.
& nbsp;
INSULATE ON THE OUTSIDE OF THE FACADE
Apart from SATE , there are other insulation systems on the outside of the sheet main facade. For example, the ventilated façade, a cavity wall type double sheet wall (the outer sheet is usually heavy too) or the storm partition type. But in rehabilitation the most common is the SATE today we will talk about it. In future articles we will talk about the other systems.
Step 1. Section of the facade without insulation:

Step 2. Section of the facade with the insulation:
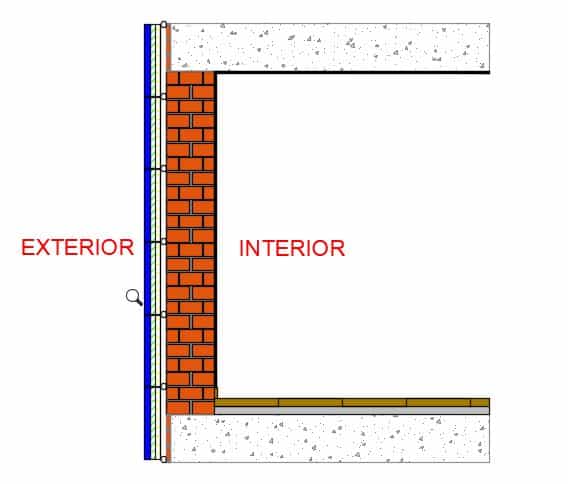
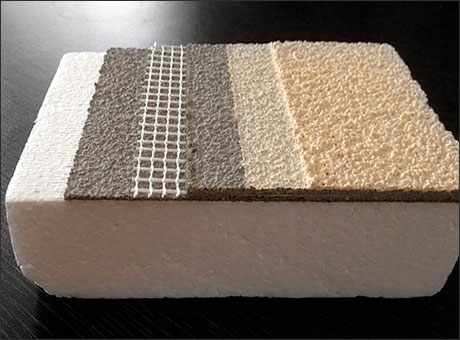
SATE INSULATION SYSTEM
This system consists of the construction of multiple layers on the exterior of the facade. This new “skin” will be composed of insulating materials covered with elements of protection to the elements. This system requires that the urban regulations of the area allow an extension of the façade towards the street since the façade will gain an approximate thickness of 7cm towards the street.
Check this article that we carry out in KAITEK ARQUITECTURA to know more details of the system
The exterior system, SATE, allows the entire building to be isolated efficiently and at the same time allows a complete restoration of the aesthetics of the facade.
During the implementation of the SATE system, it will never be necessary to affect the interior of the houses, the improvement works will take place solely and exclusively on the exterior scaffolding.
This system is the one that allows optimal energy savings, reducing annual energy consumption by an average of 55%, but it should also be noted that it is undoubtedly the most expensive system. This is the only system that allows to completely eliminate thermal bridges and that does not require any work inside the houses.
These are the main layers of the SATE system:
- Exterior finish coat, mortar monolayer for example
- Second coat of plastering
- Reinforcing mesh
- First coat of plaster
- Thermal insulation glued and fixed to the main facade sheet
One of the most notable improvements with the SATE system is the comprehensive reform that is applied to the façade, allowing enormous aesthetic changes while substantially improving the thermal insulation of the entire building. Here are some examples of the possible finishes using the SATE system.

Advantages and disadvantages of insulating from the outside
Advantages
– Allows a homogeneous insulation throughout the application area, canceling thermal bridges.
– Allows a complete aesthetic rehabilitation of the facade.
– Improved acoustic insulation.
– The facade is protected against climatic aggressions.
– It does not require any work inside the houses.
Disadvantages
– It is the system with the longest installation procedure.
– Of the three compared it is the most expensive system.
















Leave A Comment